A Beginner’s Guide to PostgreSQL Features, History, and Comparison with MariaDB and MySQL


PostgreSQL (often just called "Postgres") is a powerful, free, and open-source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS).
Think of it as a traditional relational database (like a post on What is an RDBMS?) but with significant added capabilities. It's highly respected for its:
PostgreSQL's origins trace back to a research project at the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) in the 1980s.
Founder: Professor Michael Stonebraker and his team.
Evolution:
While all three are excellent open-source databases, they are built with different philosophies.
The main difference:
MySQL and MariaDB are pure Relational Databases (RDBMS), while PostgreSQL is an Object-Relational Database (ORDBMS).
This means PostgreSQL handles complex data and advanced queries more naturally.
| Feature | PostgreSQL | MySQL | MariaDB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Type | Object-Relational (ORDBMS) | Relational (RDBMS) | Relational (RDBMS) |
| Best For... | Complex queries, data analysis, high data integrity, and applications needing advanced data types. | Web applications, read-heavy sites (like blogs/CMS), simplicity, and ease of use. | A drop-in replacement for MySQL with better performance and more features. |
| Data Types | Very rich. Natively supports JSONB, arrays, geometric, and custom types. | Good. JSON support was added later and is generally considered less robust than in Postgres. | Similar to MySQL, but often adds new features faster. |
| Concurrency | Uses MVCC (Multiversion Concurrency Control), which allows readers and writers to work concurrently without blocking. | Uses MVCC primarily for its main storage engine (InnoDB). | Also uses MVCC (via InnoDB/XtraDB). |
| SQL Compliance | Very strict. Closely follows the SQL standard. | More flexible. Easier for beginners but can lead to data integrity issues. | Aims for high compatibility with MySQL. |
| Origin Story | Started as a university project at Berkeley. | Originally developed by MySQL AB (Sweden), now owned by Oracle. | A fork of MySQL created by its original developers to ensure it remained fully open-source after Oracle’s acquisition. |
While all three are excellent open-source databases, they are built with different philosophies.
The main difference:
MySQL and MariaDB are pure Relational Databases (RDBMS), while PostgreSQL is an Object-Relational Database (ORDBMS). This means Postgres handles complex data structures and queries more naturally.
Ultimately, the best database depends on your project's specific needs.
Understanding the core differences between PostgreSQL, MySQL, and MariaDB is the first step to building a robust and scalable tech stack.
A simple diagram showing how MariaDB and PostgreSQL process queries internally:

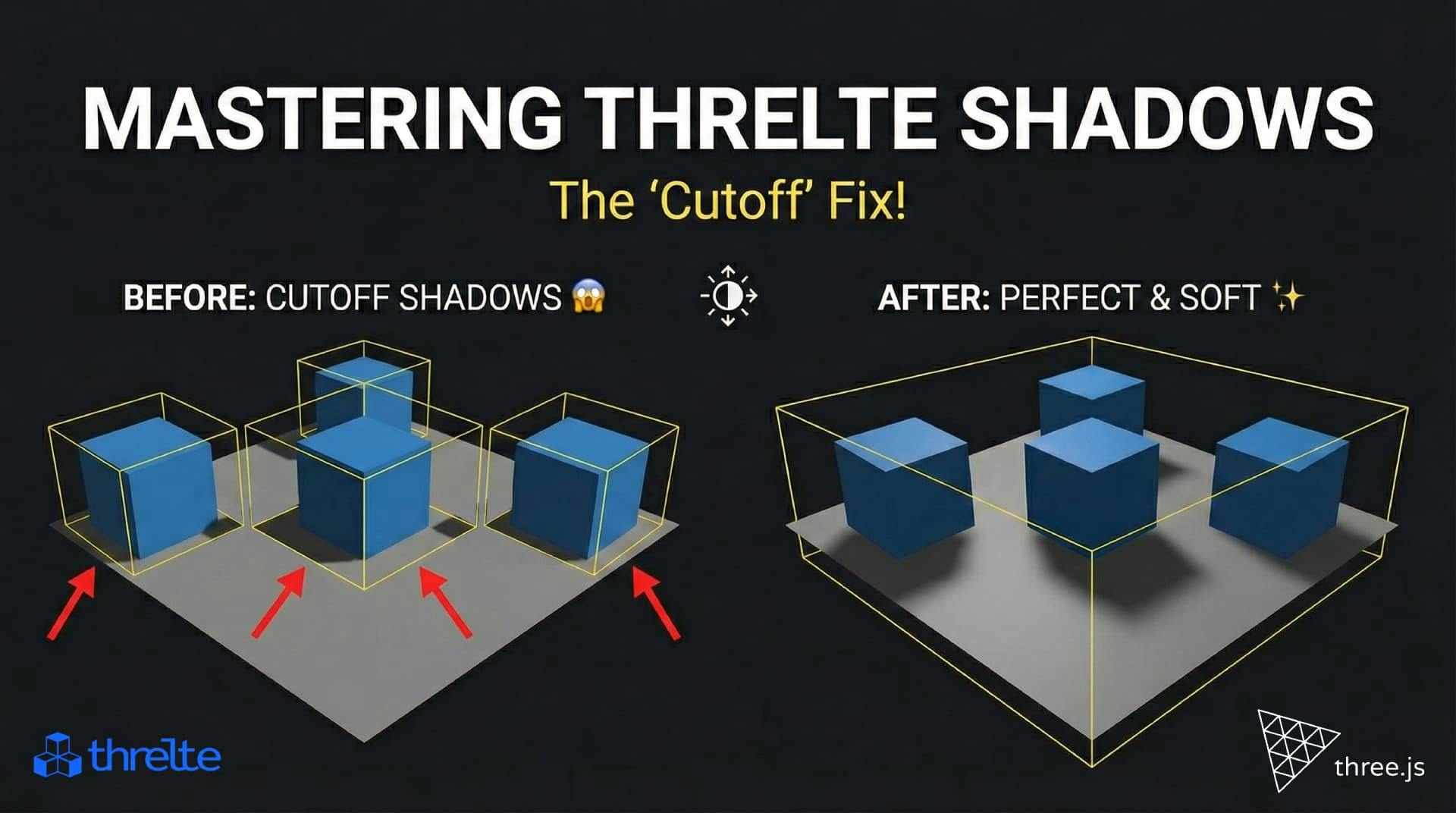
Shadows disappearing in your Threlte or Three.js scene? It’s a frustum issue. Learn how to visualize the shadow box and fix clipping instantly with this guide.

What happens when you create a DocType in Frappe? We break down the .json, .js, and .py files generated by the framework and how to use them.

Confused by Shopify's lack of a database? 🤯 Learn how Shopify stores your theme data, from simple Settings to complex Metafields. Perfect for devs moving from WP/Laravel.